Stud bolt fracture analysis
M24×170mm stud bolt, material is 35CrMoA, quenched and tempered and blackened. Installed on a liquid-filled ammonia spherical tank as a fastening bolt. After a few days, the bolt was found to have broken. The break occurs at one thread, as shown in Figure 1. The fracture was basically flat, and no obvious deformation phenomenon was observed. The entire fracture was bright and fine granular (fine grained), showing a brittle fracture shape, as shown in Fig. 2. The root area of ​​the lower part of the figure is relatively flat and is the crack initiation area; the area above the figure is rough, with steps and radial stripes, which is a fast fracture zone.
The sample was taken longitudinally near the fracture, and the matrix structure was seen as tempered sorbite. At low magnification, the flow deformation of the surface layer of the thread can be seen, and there is a depression and a slight crack at the top of the tooth. It indicates that the thread is extruded and it can be seen that there is no obvious decarburization on the surface, as shown in Figure 3.
Under scanning electron microscopy, the surface of the near-fracture thread can be seen to cover a very thick layer of corrosion products, indicating pickling and excessive blackening. In the subsurface region of the crack source region, the fracture showed cracking along the crystal, and a secondary crack and a small number of dimple morphology were observed. Shows a hydrogen-brittle appearance compared to the typical sentence.
Chemical analysis shows that the bolt material meets the 35CrMoA technical requirements.
According to the above analysis, it can be inferred that hydrogen permeation may occur due to excessive pickling or insufficient rinsing, resulting in hydrogen brittle fracture.
Since oxygen brittle fracture is a kind of delayed damage, it can be suddenly broken after being used for a period of time under stress below the yield strength of the material, which is very destructive and dangerous.
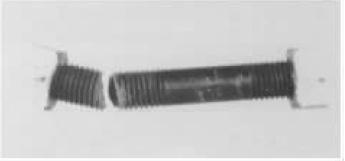
figure 1
Note: The break is located in the middle of the stud thread.

figure 2
Description: The shape of the bolt fracture is enlarged, and the brittle fracture with radial characteristics. As shown, the source of the crack is at the root of the thread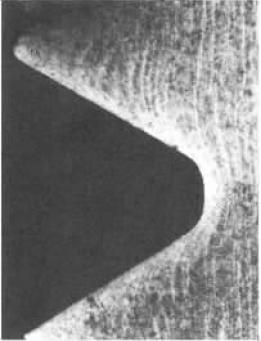
image 3

Figure 4
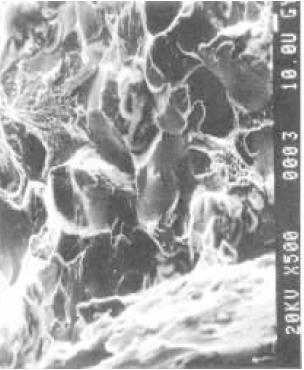
Figure 5
Note: Figure 3 shows the low-fold structure etched by 4% nitric acid solution after being cut along the longitudinal direction of the bolt.
Figure 4 is a scanning electron microscope image of the bolt surface near the fracture. There is a coating layer of corrosion products, and a muddy pattern appears in a region where the corrosion product is thickly accumulated, which is a crack of the turtle, and the corrosion product of the local area has fallen off.
Figure 5 shows the fracture morphology of the bolt with mixed characteristics of hydrogen-brittle fractures such as crystal, quasi-cleavage and dimples.
Pipe Fitting,Butt Welding Tee,Butt Welding Crosses,Stub Ends
ZHITONG PIPE VALVE TECHNOLOGY CO.,LTD , https://www.ztongvalve.com
