The efficient use of carbon dioxide under mild conditions is a topic of great scientific significance and broad application prospects. State Key Laboratory of Organometallic Chemistry, Shanghai Institute of Organic Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Ding Kuiling's research group has long been dedicated to CO2 catalytic conversion research and achieved a series of innovative results. The catalytic hydrogenation of cyclic carbonates to diols and methanol has been achieved for the first time. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 13041-13045; PCT/CN2013/073095) and successfully developed a new highly efficient catalytic system for the synthesis of carboxamides using carbon dioxide, hydrogen and organic amines as raw materials (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 6186-6189; PCT/CN2016/072342).
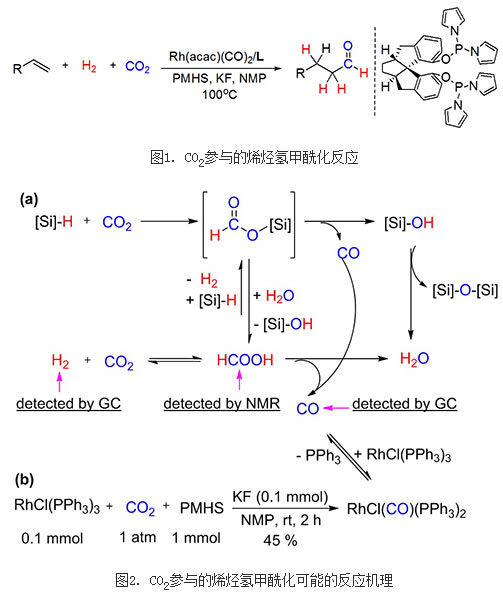
Recently, Ding Kui-ling's research group and the Lanzhou Institute of Chemical Physics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences cooperated with the Xia Chunggu Group, the State Key Laboratory of Oxo Synthesis and Selective Oxidation, and made new progress in the field of carbon dioxide catalytic conversion. They use the cheap and readily available silicon-hydrogen polymer PMHS as a reductant to reduce CO2 to CO under relatively mild conditions. The latter is directly used for the simple olefin hydroformylation reaction catalyzed by Rh, with high catalytic efficiency and Excellent regioselective separation resulted in the corresponding aldehyde product. In this field, for the first time, a one-pot synthesis of aldehydes by CO2 deoxygenation and olefin hydroformylation was achieved (Fig. 1).
Preliminary mechanistic studies (Figure 2) show that CO2 is first reduced to CO by PMHS in the Lewis basic solvent NMP, with the concomitant formation of small amounts of H2 and HCOOH. The CO generated from the reduction of CO2 is hydroformylated with H2 and an olefin catalyzed by a metal ruthenium phosphine complex to give the corresponding aldehyde. In the reaction system in which both aldehyde and CO2 are present, CO2 preferentially reacts with the silane PMHS until the latter is consumed, thereby keeping the aldehyde from being reduced to the corresponding alcohol.
To date, this is the first report of hydroformylation of olefins using CO2 as a replacement for CO and the separation of aldehydes to produce aldehydes, which shows a new way for effective chemical utilization of CO2 as a C1 resource. This part of the results was published in the "Hot Paper" in German Applied Chemistry (Angew.Chem. 2017, 129, 316-319).
The above work has been funded by the Ministry of Science and Technology, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Chinese Academy of Sciences and the Shanghai Science and Technology Commission.
5730 Led Chip,5730 Red Led Chips,White Smd Led Chips,Led Diode Lights Chip
Shenzhen Huangtai Photoelectric Co.,Ltd. , https://www.huangtailightstrip.com
